ERF-AISBL Members
The ERF-AISBL Members commit to develop and provide innovative observational, experimental and/or simulation techniques and their applications to support extended fields of Research. They also commit to offer an open and quality-based access to international scientific communities. If you would like to join us as a member, please contact us at info@erf-aisbl.eu.

Members
Countries
Meet our Members


Sincrotro Alba Elisava Alumni interior. © Copyright: ALBA Synchrotron

The Budapest Neutron Centre (BNC) is an open access facility for the domestic and international user community-a suit of reactor irradiation equipment, thermal neutron beam instruments and cold neutron spectrometers in the neutron guide hall are available and assisted by a professional team of scientists and engineers for experimental services.

Gina. © Copyright: BNC

CERIC is a distributed research infrastructure integrating and providing open access to some of the best facilities in Central and Eastern Europe, to help science and industry advance in all fields of materials, biomaterials and nanotechnology. It enables the delivery of innovative solutions to societal challenges in the fields of energy, health, food, cultural heritage and more.

Croatian 1.0 MV HVE Tandetron Accelerator © Copyright: CERIC

DESY is one of the world’s leading accelerator centres. Researchers use the large-scale facilities at DESY to explore the microcosm in all its variety – from the interactions of tiny elementary particles and the behaviour of new types of nanomaterials to biomolecular processes that are essential to life.

PETRA III experimental hall at night. © Copyright: 2009 DESY
Diamond Light Source is the UK’s national synchrotron. It works like a giant microscope, harnessing the power of electrons to produce bright light that scientists can use to study anything from fossils to jet engines to viruses and vaccines. Diamond is one of the most advanced scientific facilities in the world, and its pioneering capabilities are helping to keep the UK at the forefront of scientific research.

Dr. Matt Pankhurst studies one of the moon rock samples from the Apollo 12 & 15 missions at Diamond Light Source. © Copyright: Diamond Light Source

EGI is a federated e-Infrastructure set up to provide innovation and advanced computing services for research, including high-throughput and cloud compute and storage solutions. The EGI e-infrastructure is publicly-funded and comprises hundreds of data centres and cloud providers spread across Europe and worldwide.

Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA), a collaboration between EGI and CTA. © Copyright: Akihiro Ikeshita, Mero / TSK International

Elettra is a multidisciplinary international research center of excellence, specialized in generating high quality synchrotron and free-electron laser light and applying it in materials and life sciences. Because of its central location in Europe, Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste attracts several users from Central and Eastern European countries, where the demand for synchrotron radiation is in continuous growth.

© Copyright: Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste

Extreme Light Infrastructure ERIC is an international laser facility offering new interdisciplinary research opportunities using extreme light from the highest peak power laser sources, currently available, and dedicated to the purpose of research. These lasers and the secondary radiations derived from them will enable unprecedented discoveries across a broad range of scientific disciplines as well as societally relevant applications..

© Copyright: Extreme Light Infrastructure ERIC

The research neutron source Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II) is a central scientific institute of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) housed on the premises of the Research Centre in Garching. The FRM II provides neutrons for science, industry and medicine in four cycles of 60 days a year. The core aim of the reactor operation is to provide a high neutron flux. The FRM II has the world's best thermal ratio of performance to neutron flux and is thus one of the most effective and modern neutron sources in the world.

View of FRM II and Atomic Egg. © Copyright: W. Schürmann / TUM

GANIL, the National Grand Accelerator of Heavy Ions, is today one of the leading international laboratories for research with ion beams. Thanks to the unique nature of its facilities, GANIL is classified as a Very Large Research Infrastructure (TGIR). GANIL includes ion sources, cyclotrons, and experiment rooms that house unique high-performance detection instruments to the service of the international scientific community.

GANIL-NEDA-DIAMANT. © Copyright: Rouxel / GANIL

GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung operates a unique large-scale accelerator for heavy ions. Researchers from around the world use this facility for experiments that help them make fascinating discoveries in basic research. In addition, they continually develop new and impressive applications. GSI is a member of the Helmholtz Association, Germany's largest research organization.

GSI main entrance, Darmstadt, Germany © Copyright: GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung

The Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH (HZB) homes BESSY II, the European radiation standard for the calibration of light sources and detectors. Being a multi-disciplinary and multi-user facility, the research portfolio at BESSY II spans the range from physics, over chemistry, energy research, biology, medical and pharmaceutical research, to materials testing and cultural heritage investigations. Research at BESSY II addresses the grand challenges which most developed societies are facing.

BESSY II aerial view, HZB, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen campus at night. © Copyright: Robert Grahn / Euroluftbild.de

The Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) is an independent research center that performs research in the fields of Energy, Health, and Matter. HZDR is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates large-scale facilities in Dresden and at four other locations. These large-scale facilities are also available to external guests from around the world to help answer the decisive questions of our societies.

Ion Beam Center. © Copyright: O. Killig / HZDR

The Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS) is an institute within the Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH. JCNS uses neutrons as microscopic probe to conduct research on condensed matter and life science systems. For this purpose JCNS develops and builds neutron scattering instruments at leading national and international sources (at present: FRM II / MLZ, HFR / ILL and SNS / ORNL). It operates these instruments for its own research and offers them in the form of a user facility to a broad national and international user community.

The cold neutron three-axis spectrometer IN12, operated along with two other neutron scattering instruments by the Jülich Centre for Neutron Science at the Institut Laue-Langevin. © Copyright: ILL

LASERLAB-EUROPE is a consortium that brings together 33 leading institutions in laser-based inter-disciplinary research from 16 countries. Together with associate partners, Laserlab covers the majority of European member states. Its 22 laboratories offer access to their facilities for research teams from Europe and beyond.
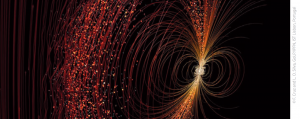
X-Ray emission from comets explained. © Copyright: F. Cruz and L. O. Silva / GoLP-IPFN, IST Lisbon, Portugal

The Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe (PRACE) is an international non-profit association with its seat in Brussels. The PRACE Research Infrastructure provides a persistent world-class high performance computing service for scientists and researchers from academia and industry in Europe. The computer systems and their operations accessible through PRACE are provided by 5 PRACE members: BSC in Spain, CINECA in Italy, ETH Zurich/CSCS in Switzerland, GCS in Germany, and GENCI in France.
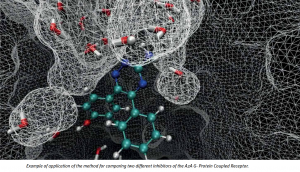
Example of application of the method for comparing two different inhibitors of the A2A G- Protein Coupled Receptor. © Copyright: PRACE

The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is the largest research centre for natural and engineering sciences in Switzerland, conducting cutting-edge research in three main areas: matter and materials, energy and environment, and human health. PSI develops, builds and operates complex, large research facilities both for in-house research, as well as for national and international access for users from academia and industry.

PSI aerial view © Copyright: Paul Scherrer Institute

The Synchrotron SOLEIL is a 3rd generation synchrotron radiation facility in operation since 2008, whose shareholders are the French public organisations CNRS and CEA. Currently, SOLEIL is delivering photons to 29 beamlines thanks to an electron beam with a current of 500 mA in top-up mode: 27 beamlines are open to users and 2 under commissioning. More than 2,000 different users, from laboratories in France, Europe and other countries come each year to perform experiments in various fields; such as surface and material science, environmental and earth science, cultural heritage, and biology.

SOLEIL aerial view © Copyright: Synchrotron SOLEIL

